Europe is again epicentre of Covid pandemic as hospitalisations increase

The coronavirus second wave has made Europe the epicentre of the pandemic once again, with the number of daily infections doubling in the past 10 days.
In France, the virus is now spreading faster than during the first wave in the spring, a scientific advisor to the government said.
France and many other European countries may be forced to resort to lockdowns again.
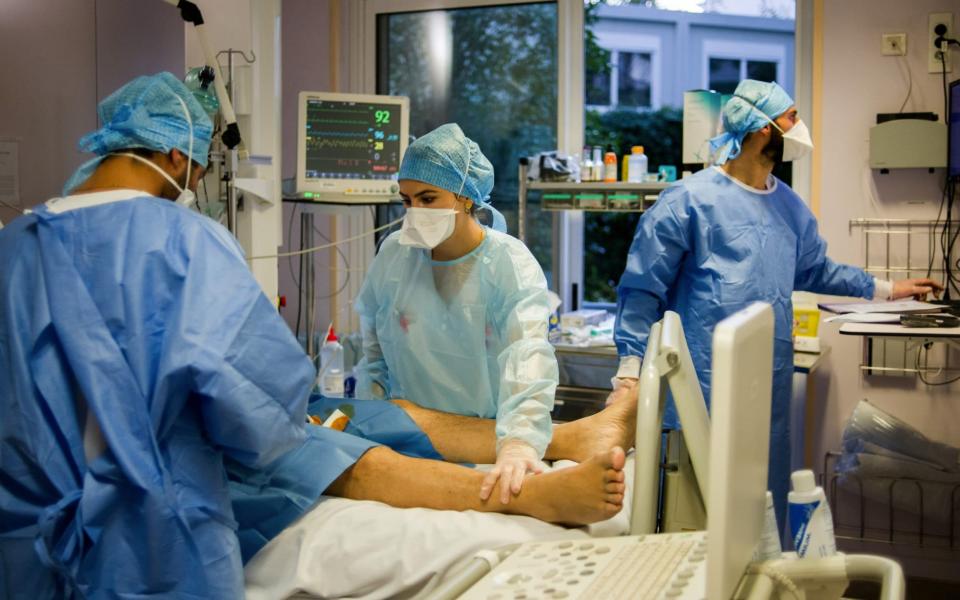
Hospitals in Europe are not yet overwhelmed by Covid-19 patients, but they are steadily filling up, according to data from the European Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (ECDC).
The numbers of coronavirus patients in Britain and Belgium have doubled in the past two weeks. The Czech Republic has the highest number of hospital cases per capita, according to the ECDC, amid alarm over the increasing number of its health workers falling ill.
Poland and Bulgaria are also badly affected and people across much of Europe are now more likely to be hospitalised than in the United States, the data suggests.
It shows that the pandemic is still dangerous despite earlier suggestions that the virus had become less deadly or affected only the elderly. In France, about 35 per cent of intensive care cases are under 65.
Poland has turned its largest sports stadium into a temporary 500-bed field hospital.
Daily infections in Europe exceeded 200,000 for the first time on Thursday, surpassing the combined total of those in America, Brazil and India, Reuters reported. Many European countries reported their highest single-day case tallies this week.
Leaders in France, Germany and other countries have warned that their health systems are facing an overload.
Arnaud Fontanet, a senior scientific adviser to the French government, said the virus is now spreading faster than during its initial outbreak. "The virus is circulating more quickly,” he warned, adding that the fight against the disease would be “a marathon”.
The government has expanded a 9pm coronavirus curfew to cover more than two-thirds of France’s population.
The current surge in infections is attributed partly to more relaxed behaviour during the summer, when numbers fell. Families travelled on holiday, students returned to universities and large gatherings resumed, allowing Covid-19 to spread.
Dr Fontanet said the French authorities had succeeded in bringing the virus under control by the end of June, with the number of hospitalisations remaining low until the end of August, which gave a false sense of security, although cases were increasing.
“Then there was one cold week in September and all the indicators went the wrong way again, all over Europe. The virus spreads better in the cold because we live more inside,” he said.
Jean Castex, the prime minister, has hinted that another lockdown may be imminent unless the pandemic is brought under control. Acknowledging that the curfew caused hardship, he warned people to observe restrictions on social gatherings, maintain physical distancing and work from home to avert the need for “much harder measures”.
France, Italy, Austria, The Netherlands, Croatia, Slovenia and Bosnia all reported record numbers of daily coronavirus cases this week.
French authorities reported an all-time high of 41,622 new confirmed Covid-19 cases on Thursday, taking the nation's seven-day average to 25,480 infections per day.
Germany, which reported more than 10,000 daily cases for the first time on Thursday, extended travel warnings for Switzerland, Ireland, Poland, most of Austria and Italy, including Rome.
Pharmacies in France and a number of other European countries have been running short of flu vaccines as people followed government advice to get inoculated to reduce the risk of a potentially lethal “twindemic”.

