Sky islands — teeming with new species — found in Southeast Africa. See the creatures
On a strip of mountains in southeast Africa, rainforest and grassland creatures are cut off from the rest of the world.
The range stretches from northern Mozambique to Mount Mulanje in Malawi, the continent’s second-highest peak.
They were formed millions of years ago as the Earth’s crust pushed upward and torrential rainfall cut through the rock, leaving large sections of forest separated from lower elevations.
They are called granitic inselbergs, or “islands in the sky” — and they’ve just been explored.
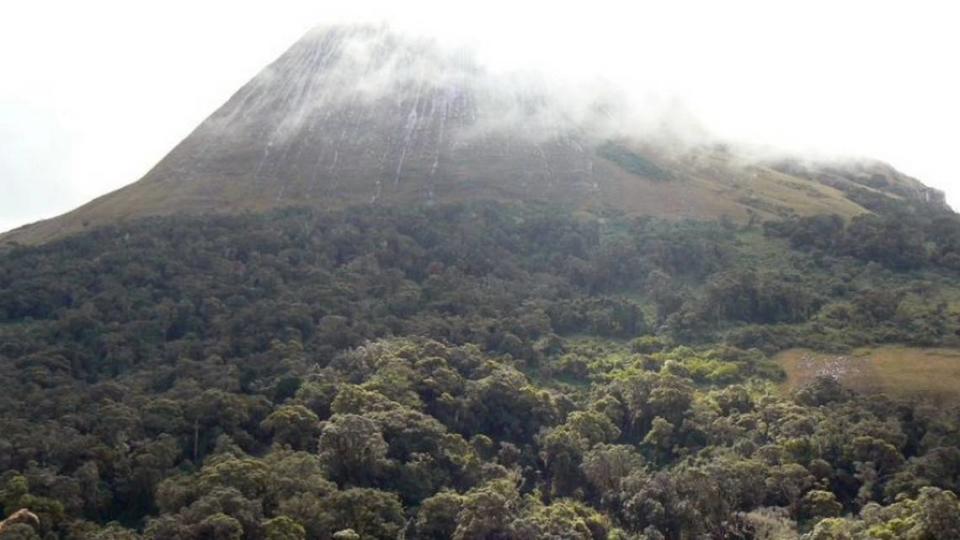

In a new study, researchers from around the world detail hundreds of species that are entirely unique to this region, some of which have never been seen before.
The study was published March 12 in the journal Scientific Reports.
“It took decades of international collaboration to gather sufficient evidence to define the ecoregion. We documented hundreds of previously undescribed species, and researched the geology, climate and genetic history of the ecosystems, to piece together what makes these mountains so unique,” study author Julian Bayliss, from Oxford Brookes University in England, said in a news release.
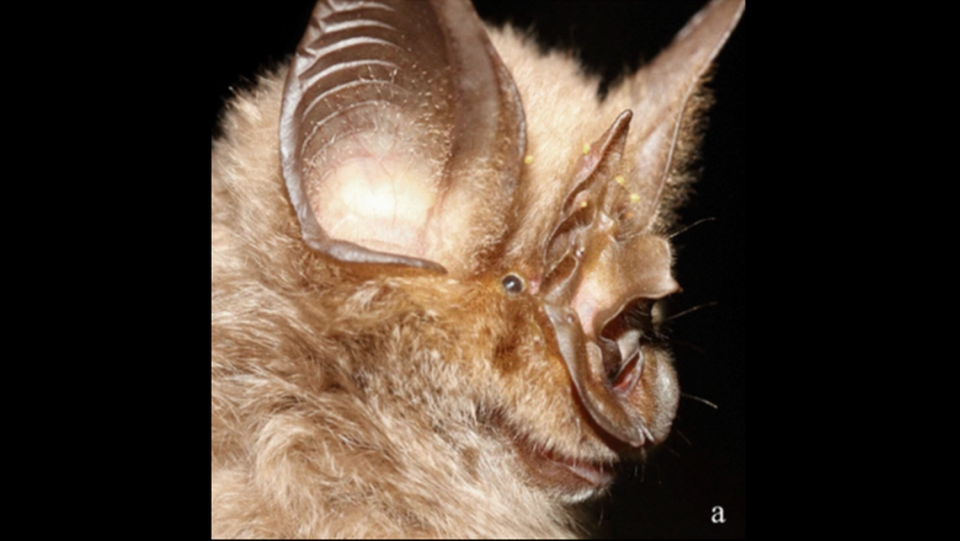
This included 127 plant species, 45 species of vertebrates like amphibians, reptiles birds and mammals, and 45 species of invertebrates like butterflies and crabs, according to the study.
The researchers identified 117 plant species that are strictly endemic to the mountains, meaning they don’t exist anywhere else on the planet. They also discovered species that are found in other regional locations, according to the study.
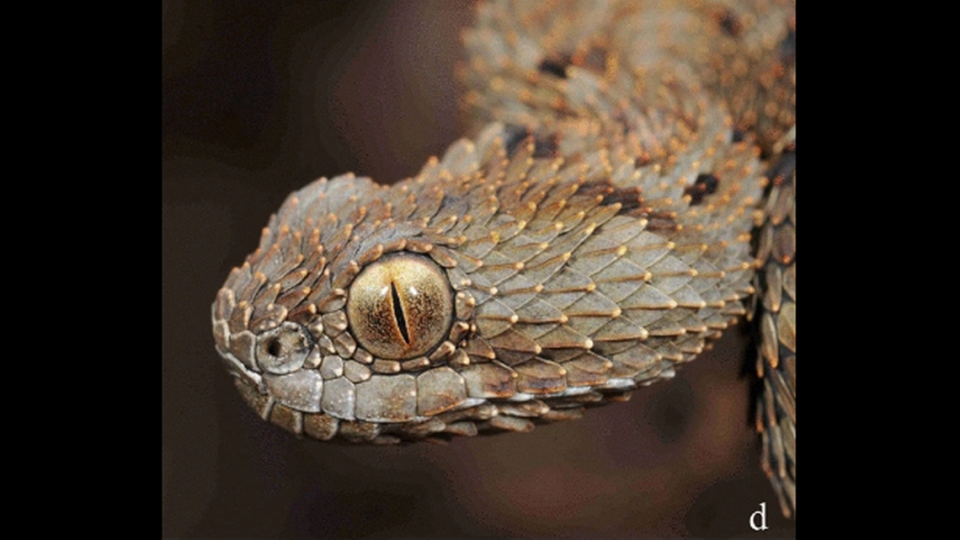
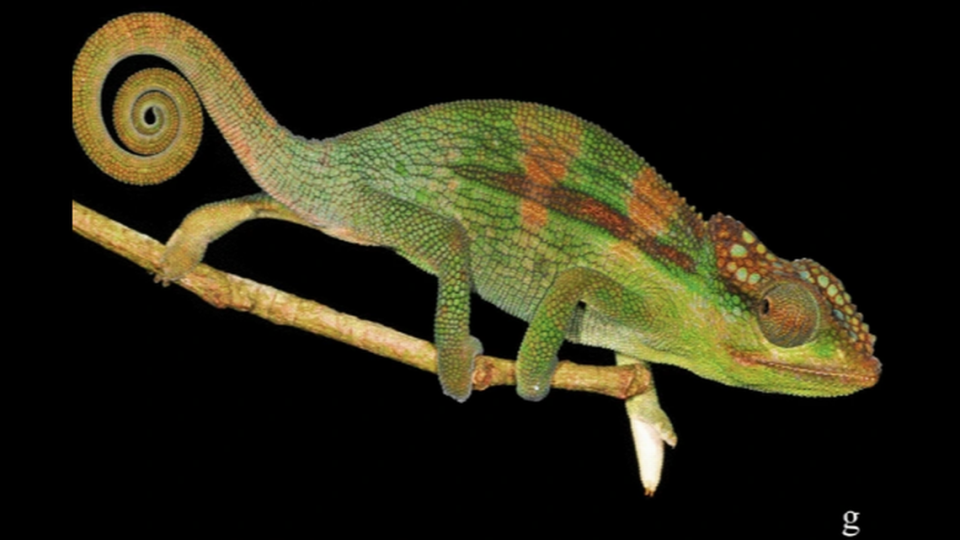
The animals were also unique, including species that were only distantly related to any other known creatures, meaning they had been genetically isolated for a long time.
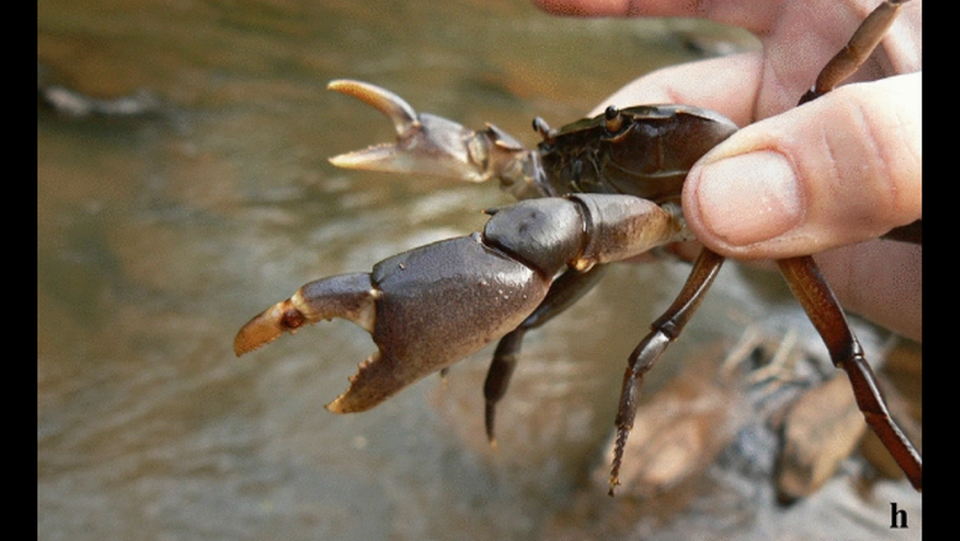
A bush viper, for example, was likely separated from other vipers for 15 million years, evolving into a completely new species on the sky islands, the study said. Another species of freshwater crab was isolated for nearly 5 million years.

“The ecoregion is fragmented across small isolated pockets of rainforest, montane grasslands and shrublands, each with their own unique, but distantly related, plants and animals. There is so much more to discover, but many of these species may go extinct before we can record them,” study co-author and biologist from University of Lúrio in Mozambique, Harith Farooq, said in the release.
The researchers believe the environment is so different from the land that surrounds it, that the sky islands should be designated as a completely new ecoregion: the South East Africa Montane Archipelago.

The new classification would allow for protection of the ecoregion, the researchers said, something that is paramount as the rainforest continues to shrink.
Just in the time since the researchers began the study, about 20 years ago, the area has lost anywhere from one-fifth to half of its forest, the researchers said.
“Encouraging conservation of the South East Africa Montane Archipelago is paramount as it’s clear we’ve only begun to scratch the surface of what we can learn about this diverse region as well as consider how these learnings can be applied to global biodiversity conservation efforts,” co-author Gabriela Bittencourt, a researcher at the Natural History Museum in London, said in the release.

Mozambique and Malawi are in the southeastern region of Africa.
‘Dwarf’-like mountain creature seen snacking on plants in Peru. It’s a new species
Orcas covered in scars left by ‘cookiecutter sharks’ may be new population, study says
Pregnant creature — with hairy lips and yellow ears — discovered as new species
Adorable — and rare — horned creature born at UK zoo. See his ‘wobbly’ first steps


